Ammonium Arsenite Manufacturing Plant Project Report 2025: Manufacturing Plant Setup and Operations
Introduction
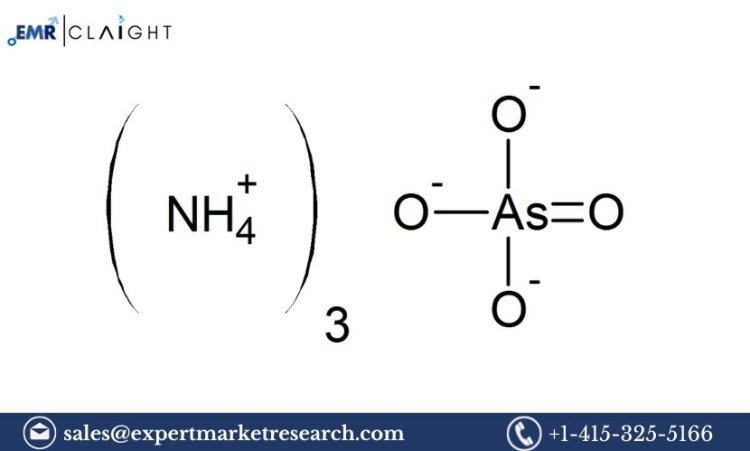
Ammonium Arsenite, commonly known as "Paris Green," is a chemical compound primarily used in the production of pesticides and herbicides. It is a potent arsenic-based chemical, with a variety of applications in agricultural, industrial, and chemical industries. The demand for ammonium arsenite has grown in response to the increasing need for effective pest control in agriculture and the development of industrial products. An Ammonium Arsenite Manufacturing Plant Project Report provides a detailed blueprint for setting up an ammonium arsenite production facility, addressing the entire process from raw material procurement to the final product's packaging and distribution. This report includes market analysis, production methods, equipment needs, financial considerations, and compliance with environmental and safety regulations. It serves as a comprehensive guide for those looking to establish a manufacturing plant for ammonium arsenite.
Market Overview and Demand
Ammonium arsenite is primarily used as an insecticide and pesticide, particularly in controlling pests in crops. Although less commonly used in residential pest control today due to safety concerns, its applications in agriculture, particularly in the form of Bordeaux mixture, continue to drive its demand. It is also used in certain industrial processes, such as dye manufacturing.
1. Agriculture and Pest Control
Ammonium arsenite is most commonly utilized in the agricultural sector for controlling a wide variety of insects, including aphids, weevils, and caterpillars. Its use as a pesticide, however, has diminished over the years due to concerns over arsenic toxicity, with many farmers opting for less toxic alternatives. Despite these concerns, it continues to be used in certain parts of the world due to its efficacy and cost-effectiveness.
2. Dye Manufacturing and Textile Industry
Ammonium arsenite is also used in the production of certain types of dyes and pigments, particularly in the textile industry. In this sector, the compound is used to create vivid green pigments that are resistant to fading and washing.
Get a Free Sample Report with Table of Contents@
3. Industrial Applications
In addition to its agricultural and textile uses, ammonium arsenite has applications in other industrial sectors. These include the production of wood preservatives, leather tanning, and as a mordant in certain chemical processes.
4. Regulatory Trends
The use of ammonium arsenite is subject to increasing regulation due to its toxicity, especially in terms of environmental impact and health safety. As environmental concerns grow, governments are implementing stricter regulations for the use and disposal of such chemicals, which may affect the market demand.
5. Growing Need for Safe Alternatives
While ammonium arsenite continues to be used, there is a significant push in the agricultural industry for safer, more sustainable alternatives to arsenic-based pesticides. This trend could influence the future demand for ammonium arsenite, with producers needing to innovate in response to market changes.
Location and Infrastructure
Selecting the right location for the Ammonium Arsenite Manufacturing Plant is critical for ensuring smooth operations, efficient distribution, and compliance with regulatory requirements. Below are key factors to consider when choosing the location for the plant:
1. Proximity to Raw Materials
The key raw materials for ammonium arsenite production include ammonium hydroxide and arsenic compounds such as arsenic trioxide or arsenic acid. Choosing a location near suppliers of these chemicals will reduce transportation costs and ensure a reliable supply chain.
2. Access to Transportation and Distribution Networks
The location should have good access to transportation routes, including highways, railroads, and ports, to ensure efficient distribution of the finished product. Since ammonium arsenite may be sold to agricultural, industrial, and chemical companies, accessibility to key markets is essential.
3. Utilities and Power Supply
Ammonium arsenite manufacturing requires significant amounts of energy for heating, cooling, and powering machinery. The plant should be located in an area where electricity, water, and natural gas are readily available at competitive prices to keep operational costs in check.
4. Skilled Workforce Availability
A skilled workforce is necessary for maintaining plant operations and ensuring that production processes run smoothly. Labor costs should be competitive, and the location should have access to qualified chemical engineers, safety personnel, and production workers.
5. Regulatory Compliance
Regulatory compliance is crucial, especially for a chemical manufacturing plant dealing with toxic substances. The location should comply with both national and international environmental regulations, health and safety standards, and local zoning laws. Proximity to regulatory bodies can help ensure quick approvals and avoid potential delays in the setup process.
Production Process
The manufacturing process for ammonium arsenite typically involves the reaction between ammonium hydroxide and arsenic compounds. Below is a step-by-step breakdown of the production process:
1. Preparation of Raw Materials
The key raw materials for producing ammonium arsenite are ammonium hydroxide (NH₄OH) and arsenic trioxide (As₂O₃) or arsenic acid (H₃AsO₄). These materials need to be prepared in the right proportions to ensure the correct chemical reaction.
2. Synthesis of Ammonium Arsenite
Ammonium arsenite is formed by the reaction of ammonium hydroxide with arsenic compounds.
3. Purification and Filtration
The resulting ammonium arsenite solution needs to be purified to remove any unreacted raw materials or by-products. This is usually done through filtration or centrifugation to remove impurities.
4. Drying
After purification, the ammonium arsenite solution is dried to remove excess water content, leaving behind solid ammonium arsenite. Drying is typically carried out in rotary dryers or under controlled heat conditions to avoid degradation of the chemical.
5. Grinding and Sieving
Once the ammonium arsenite is dried, it is ground into a fine powder. This powder is then sieved to achieve the desired particle size for different applications. The sieving process helps remove any larger particles or impurities, ensuring a consistent product.
6. Packaging
The final ammonium arsenite product is carefully packaged in airtight containers to prevent contamination and degradation. Packaging is typically done in sealed, moisture-resistant bags or drums, and the product is labeled with relevant safety warnings due to its toxicity.
Equipment and Technology Requirements
The production of ammonium arsenite requires specialized equipment to handle hazardous materials and ensure the chemical reactions are carried out safely and efficiently. Here are the key pieces of equipment needed:
1. Reaction Vessel
A high-quality reaction vessel is essential for the safe mixing of ammonium hydroxide and arsenic compounds. The vessel should be designed to handle corrosive and toxic chemicals and be able to withstand high temperatures and pressures.
2. Filtration and Purification Units
Filtration equipment is necessary to separate impurities and by-products from the ammonium arsenite solution. This may involve membrane filtration, centrifugation, or other separation technologies.
3. Drying Equipment
The drying equipment ensures that the ammonium arsenite is thoroughly dehydrated before packaging. Common drying methods include rotary dryers or tray dryers, depending on the required production capacity.
4. Grinding and Sieving Equipment
Grinding mills and sieves are used to reduce the size of the dried ammonium arsenite into fine powder and ensure uniform particle size. This equipment is crucial for maintaining the product's quality and consistency.
5. Packaging Machines
Packaging machines are used to fill and seal the ammonium arsenite powder into airtight containers. These machines should be capable of handling large volumes efficiently and ensuring that the product is properly sealed to maintain its quality.
Regulatory Compliance and Safety Standards
Given the toxic nature of ammonium arsenite, it is subject to strict regulations to ensure the safety of workers, consumers, and the environment. Below are key safety and regulatory considerations:
1. Environmental Regulations
Ammonium arsenite production can result in toxic emissions and waste. The plant must have waste treatment systems in place to neutralize or safely dispose of any by-products, including arsenic-based waste. Environmental compliance will involve air, water, and waste management systems to adhere to local and international environmental standards.
2. Health and Safety Standards
The plant must comply with occupational health and safety regulations to protect workers from exposure to toxic substances. Workers should be provided with personal protective equipment (PPE), and regular safety training should be conducted to minimize accidents and exposure.
3. Toxic Substance Handling
Ammonium arsenite is a highly toxic substance, and proper handling protocols must be in place. This includes the safe storage of raw materials, proper labeling, and the use of ventilated equipment to prevent exposure to arsenic dust or vapors.
4. Regulatory Certifications
Depending on the region of operation, the plant may need certifications related to chemical manufacturing, such as ISO certification for quality control, as well as adherence to local pesticide manufacturing regulations.
Financial Planning and Investment
Setting up an ammonium arsenite manufacturing plant requires a significant capital investment. Below are the financial considerations:
1. Initial Capital Investment
This includes the cost of land, infrastructure, machinery, and raw materials. A detailed feasibility study is essential to determine the total investment required for setting up the plant.
2. Operational Costs
Ongoing costs include raw material procurement, labor, utilities, equipment maintenance, and safety management. Efficient cost management will be key to ensuring the plant remains profitable.
3. Revenue Generation
Revenue is generated by selling ammonium arsenite to agricultural, chemical, and industrial sectors. Profit margins will depend on production capacity, market demand, and operational efficiency.
4. Funding Options
Securing funding for the project may involve loans, equity investments, or government incentives. A solid business plan, including market analysis and financial projections, will be necessary to attract investors or financial institutions.
Media Contact
Company Name: Claight Corporation
Contact Person: Lewis Fernandas, Corporate Sales Specialist — U.S.A.
Email: sales@expertmarketresearch.com
Toll Free Number: +1–415–325–5166 | +44–702–402–5790
Address: 30 North Gould Street, Sheridan, WY 82801, USA
Website: www.expertmarketresearch.com
Aus Site: https://www.expertmarketresearch.com.au
What's Your Reaction?


















